Table of Contents
In a time when it’s more important than ever to stay connected, the technology that powers our connectivity is evolving fast. The eSIM card is a groundbreaking innovation that’s changing how we connect to networks and use our devices. This in-depth guide explains everything you need to know about eSIM cards—what they are, how they work, and why they’re quickly becoming the new standard in mobile connectivity.
1. How SIM Technology Has Changed Over the Years
From SIM Cards to eSIMs
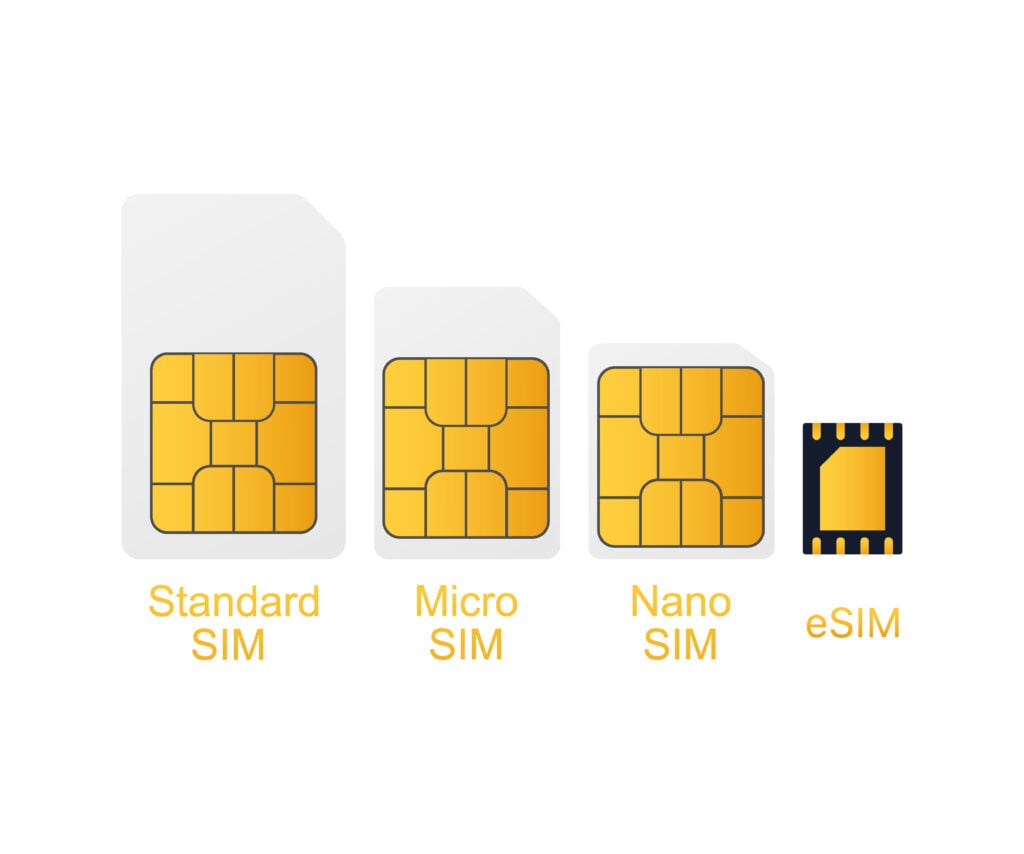
The Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card has been essential in mobile phones for decades. It stores the critical data that connects your device to a mobile network. Traditional SIMs have evolved from standard to micro and nano sizes, but all require manual handling to activate or change networks.
The eSIM (embedded SIM) changes this by removing the need for a physical card. Built directly into your device’s hardware, it can be programmed or updated remotely, offering greater flexibility and ease of use.
What it Does in the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) industry was among the first to adopt eSIM technology. Devices like smartwatches, drones, and industrial sensors benefit from eSIMs due to their compact size and remote management. Embedded connectivity allows manufacturers to create smaller, smarter, and more efficient products.
2. Finding Out More About eSIM Technology
What Does an eSIM Do?
An eSIM is a rewritable SIM card embedded into your device’s motherboard. It doesn’t need a physical slot and can store multiple carrier profiles, allowing you to switch providers without changing cards.
How Does It Work?
eSIMs are based on the Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card (eUICC) standard. Using Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP), carriers can send your SIM profile to your device over the internet. A QR code or activation code links your device to the network.
Details About Technology
- Size: Much smaller than nano-SIM cards.
- Standards: Compliant with GSMA eSIM specifications.
- Security: Supports advanced encryption and verification methods.
3. Benefits of eSIM Cards
Simple to Use and Adaptable
- Multiple Profiles: Store multiple carrier profiles and switch easily between them.
- Easy Activation: Activate service via a QR code or app—no physical handling required.
- Global Roaming: Effortlessly switch to local carriers when traveling abroad.
How Devices Make Good Use of Space
- Design Freedom: Free up space in devices for larger batteries or new features.
- Durability: Less prone to wear or damage since there’s no removable slot.
More Secure Features
- Tamper-Resistant: Harder to remove or duplicate due to its embedded nature.
- Remote Management: Lock or erase your eSIM remotely if your device is lost or stolen.
4. How to Turn on the eSIM
What Does “Remote SIM Provisioning” Mean?
Remote SIM Provisioning enables your carrier to send your SIM profile to your device securely over the internet. No physical card or manual installation is needed.
How to Activate: Step-by-Step Guide
For iOS Devices
- Check Compatibility: Make sure your iPhone supports eSIM (e.g., iPhone XS or later).
- Get Activation Code: Request a QR code or activation code from your carrier.
- Open Settings: Go to Settings > Cellular > Add Cellular Plan.
- Scan QR Code: Use your camera to scan the code provided.
- Label Your Plans: Customize names if you have multiple plans.
- Set Default Line: Choose your default line for calls, texts, and data.
For Android Devices
- Check Compatibility: Confirm your device supports eSIM (e.g., Google Pixel 3 or later).
- Get Activation Code: Obtain a QR or activation code from your carrier.
- Open Settings: Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Mobile Network.
- Add Carrier: Tap + to add a new network.
- Scan QR Code: Follow instructions to scan the code.
- Complete Setup: Finalize settings and confirm activation.
5. eSIMs Compared to Regular SIM Cards
| Feature | Traditional SIM Card | eSIM |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Card Required | Yes | No |
| Multiple Profiles | No | Yes |
| Device Space | Requires Slot | Embedded, saves space |
| Activation | Physical Handling | Remote Provisioning |
| Security | Removable | Embedded, more secure |
Pros and Cons
eSIM Pros:
- Greater flexibility
- Space-saving design
- Enhanced security
eSIM Cons:
- Limited support from some carriers
- Not all devices are compatible
Traditional SIM Pros:
- Widely supported globally
- Easy to move between devices
Traditional SIM Cons:
- Inconvenient when switching carriers
- Can be lost or physically damaged
6. How eSIM Technology Is Used Around the World
Rates of Adoption by Area
- North America: Rapid growth; major carriers now support eSIM.
- Europe: High adoption, especially in countries like the UK and Germany.
- Asia-Pacific: Adoption is growing slowly in emerging markets.
Case Studies of eSIM Use
- Automotive Industry: Cars use eSIMs for GPS, emergency help, and in-car Wi-Fi.
- Wearables: eSIMs let smartwatches connect to networks without phones.
The Laws and Rules
Each country has its own regulations, which affects the speed of eSIM adoption. Some nations have strict telecom laws that slow progress, while others support faster innovation.
7. Different Ways to Use eSIM
Vehicles
- Connected Cars: Access real-time traffic updates and remote diagnostics.
- Fleet Management: Easily track and manage business vehicle fleets.
Wearables and Health Tech
- Smartwatches: Use cellular connectivity without needing a smartphone.
- Medical Devices: Enable remote monitoring and emergency alerts.
Industrial Applications
- Smart Manufacturing: Connect machines for more efficient production.
- Logistics: Improve visibility and tracking across the supply chain.
8. What Will Happen Next?
5G Networks and eSIM
The combination of eSIM and 5G brings faster, more reliable connections with low latency. This is critical for developments in smart cities, IoT, and self-driving vehicles.
Impact on the Growth of IoT
eSIMs simplify large-scale IoT deployment by enabling remote setup and management, which is key for industries with many connected devices.
Possible Issues Ahead
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring eSIM profiles work across devices and networks.
- Market Resistance: Some users and carriers may hesitate to adopt the new tech.
- Privacy Issues: Protecting personal data in a highly connected environment.
9. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I use an eSIM and a physical SIM at the same time?
Yes, many devices support dual SIM functionality, allowing both an eSIM and a physical SIM card to be used simultaneously.
2. How do I know if my device supports eSIM?
Check your device specs on the manufacturer’s website or in the user manual. Devices like the iPhone 14 and Google Pixel series support eSIM.
3. Is eSIM secure?
Yes. eSIMs use advanced encryption and are embedded in the device, making them harder to tamper with.
4. What happens if I reset my device?
Resetting your device may delete your eSIM profiles. You’ll need to contact your carrier to reactivate or restore them.
5. Are there any extra fees for using eSIM?
The eSIM itself usually has no extra cost, but some carriers may charge for activation or profile downloads. Always check with your carrier.
10. Conclusion
The eSIM card is more than just a tech upgrade—it’s a step into a more connected and adaptable future. With no physical limitations, eSIMs provide unmatched ease of use, making them ideal for travelers, tech-savvy users, and businesses managing connected devices.
As we move toward a fully connected world, using eSIM technology puts you ahead of the curve. Check your device compatibility, explore your carrier’s offerings, and make the switch today.
We’re glad to have you here—now that you know the importance of using eSIM, explore our services and get connected the smart way!
eSIM Plans for Destinations in This Article
Travel smarter with eSimy
Instant eSIM plans for 165+ countries. Activate in seconds, connect before you land.
Get Your eSIM Now



